【】How to Draw Lewis Dot Structure
Hello, Everyone! today we are going to know how to draw Lewis structure or Lewis dot diagrams for atoms,ions and simple molecules.
How to find out valence electrons of an element?
Before I begin, I would like to ask you a question:how many valence electrons does chlorine have?
For getting the answer of that question we need to look at the periodic table.
Notice that within any given column all the elements have the same number of valence electron.
To get valence electron's number, all we have to do is to count the columns starting from left.Skip the transition metals and bear in mind that the only exception to this is helium atom, which has only 2 valence electrons(duet) ,not 8.
Now find chlorine in the periodic table. Remember that Chlorine's symbol is Cl. See it in the 7th column.
That indicates us that it has 7 valence electrons.
If you do electronic configuration of chlorine,
then you will see that the outermost shell has 7 electrons,which are called valence electrons of chlorine.
Remember that the maximum principal quantum number indicates valence shell of chlorine.The electrons of valence shell are called valency electrons.
However,In Lewis structure or diagram,we use dot(.) to represent valence electron.So the Lewis dot structure of Chlorine is the symbol Cl with 7 dots around it.
When you draw the dots, don't just put them anywhere.Instead,imaginea square around the element's symbol.
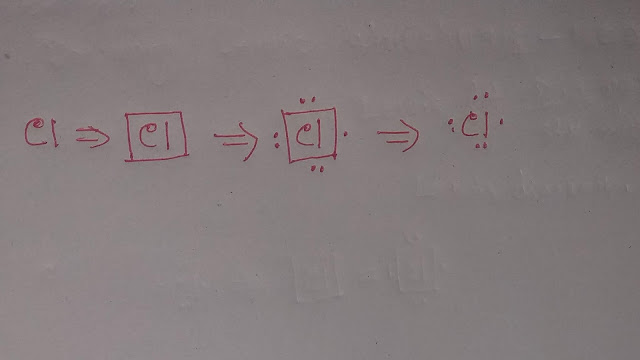
That dots should be drawn on the four sides of the square with no more than two dots on any side.
Now practise drawing the Lewis structures of a few elements just to make sure you've got it.
This is the Lewis structure of hydrogen(above),which has only one valence electron.
This is Carbon,
which has 4 valence electrons.So the lewis structure of Carbon is given here.
For carbon and other small atoms, we imagine that there are four coordination sites which accommodate electrons or bonds because this is how carbon can fill it's octet or outermost shell that is called valence shell.If we want to draw the valence electrons,we put one in each coordination site first before we pair them up.So carbon will look like this.
This is oxygen,
which has 6 valence electrons.So the Lewis dot structure of oxygen atom is given here.
Also remember that elements in the same group will have similar looking Lewis dot symbol because they have the same number of valence electrons.See picture.
•Lewis dot structures( Lewis structures) are often used to represent covalent bonding in molecules and ions.
•In covalent bonding, atoms share valence electrons for getting a full octate or duet,that is every non-metal element wants 8 valence electrons except for hydrogen, which only wants two valence electrons.
•Lewis diagram of H₂ is given below-
•A hydrogen atom(H•) atom has one valence electron,but it wants to have two.So,in order to satisfy its desire for another electron,two hydrogen atoms will share their electrons with each other.
And the amazing thing in the world of atoms is that the shared electrons are counted as owned by both atoms.
H:H
That means that both hydrogen atom are happy because they both satisfy the duet rule.
Now we normally draw hydrogen and other molecules like this(H-H) with line to represent shared electrons (H-H) and dots only (He:)
for non-bonding electrons.
These two diagrams{(H:H) and (H-H)} of hydrogen molecule are equivalent because one line(-)which is a single bond, represents 2 shared electrons.
In the same way,two lines(=) between atoms (O=O) would be a double bond and would be the sharing of 4 electrons.
🔊 1 line=single bond=2 electrons
🔊2 lines=Double bond=4 electrons
🔊3 lines=Triple bond=6 electrons
Here I am going to give you an example of a molecule with a double bond.This molecule is oxygen which looks like this:
.
We notice carefully that in this Lewis dot diagram both oxygen atoms in oxygen molecule have 8 valence electrons,actually 4 from the double bond and 4 from the lone pairs of electrons.
●However,2 dots over oxygen together are called a lone pair of electrons.
●Notice that some molecules contain triple bonds,which we write by using 3 lines that represent the sharing of 6 electrons.
Let me show you an example of a molecule with a triple bond.This molecule is nitrogen which look like the above.
Again,look carefully that both nitrogen atoms have 8 valence electrons,6 from the triple bond and 2 from the lone pairs of electrons.
Now we have come to the main part.How do you actually draw the lewis diagram of a molecule?
Let's get started with Water,H₂O.
Lewis Structure of Water(H2O)
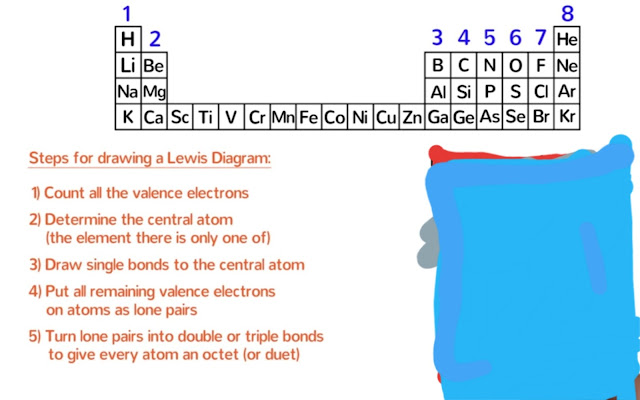
●Here is the 5 steps that you need to follow when drawing the Lewis dot diagram of a molecule.
Step-1
First of all ,we need to count all the valence electrons in the molecule.
For water ,H₂O , each hydrogen has one electron and we multiply that by two because there are two hydrogen in H₂O molecule.
The oxygen has 6 valence electrons.Now add the valence electrons of two hydrogen and one oxygen in water molecule together.So we are getting a total of 8 valence electrons for the water, molecule.
Step-2:
Now we need to determine the central atom.The central atom is the one that all of the others atoms will be bonded to.It is usually the element that there is only of.
In case of H₂O, oxygen (O) is the central atom because there are 2 hydrogens and only one oxygen.Here we choose oxygen as the central atom and we need write it in the middle.
Step-3:
Draw single bond to the central atom.
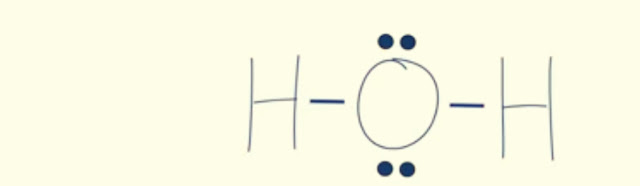
H-O-H
For H₂O,we started with 8 valence electrons.So far,we have used four electrons for the two single bonds.So,we have four more electrons (left over).
Step-4:
Now we will put 4 of those remaining electrons on oxygen instead of hydrogen because hydrogen is already happy with 2 valence electrons.
Remember that never give hydrogen more than two valence electrons.Everyone else wants 8 electrons ,but hydrogen only wants two.
Step-5:
If necessary,turn lone pairs into double or triple bonds to give every atom an octate (or duet for hydrogen).
Look at the water,already all the atoms in water are happy because each hydrogen has 2 electrons and the oxygen has 8 electrons.Everyone is happy.And there is no need for double or triple bonds,which means that our lewis dot diagram of water is now complete.Step-1
First of all ,we need to count all the valence electrons in the molecule.
For water ,H₂O , each hydrogen has one electron and we multiply that by two because there are two hydrogen in H₂O molecule.
The oxygen has 6 valence electrons.Now add the valence electrons of two hydrogen and one oxygen in water molecule together.So we are getting a total of 8 valence electrons for the water, molecule.
Step-2:
Now we need to determine the central atom.The central atom is the one that all of the others atoms will be bonded to.It is usually the element that there is only of.
In case of H₂O, oxygen (O) is the central atom because there are 2 hydrogens and only one oxygen.Here we choose oxygen as the central atom and we need write it in the middle.
Step-3:
Draw single bond to the central atom.
H-O-H
For H₂O,we started with 8 valence electrons.So far,we have used four electrons for the two single bonds.So,we have four more electrons (left over).
Step-4:
Now we will put 4 of those remaining electrons on oxygen instead of hydrogen because hydrogen is already happy with 2 valence electrons.
Remember that never give hydrogen more than two valence electrons.Everyone else wants 8 electrons ,but hydrogen only wants two.
Step-5:
If necessary,turn lone pairs into double or triple bonds to give every atom an octate (or duet for hydrogen).
 |
Now learn to draw the lewis structure of CO in just 5 steps.Click here.










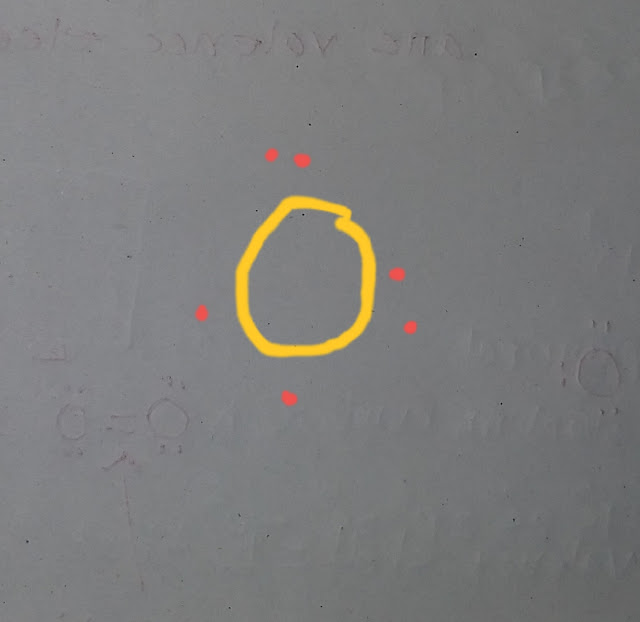










Comments
Post a Comment