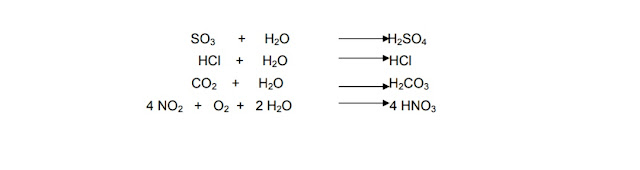
Global Warming || What is Global Warming?
Global Warming || What is Global Warming? The warming up of the earth’s surface due to green house effect is termed as global warming. Causes of Global Warming CO2 and other green house gases present in the atmosphere trap the infrared radiation from the sun and do not allow the radiations to escape. Hence the earth’s surface is warming up more and more. Effects of global warming caused by Green house effect: 1. Evaporation process of surface water is enhanced very much due the increase in temperature of earth’s surface which leads to drastic seasonal change. Some region of the world would become dry. 2. Sea level is increased due to melting of glaciers. Hence, low lying land areas will be submerged under sea water. 3. Food production is mainly affected and it leads to draught. 4. The tropical diseases like malarial fever, dengue fever and cholera will spread to the other parts of the world. 5. It causes drastic change...